MapReduce是一种编程模型,用于大规模数据集(大于1TB)的并行运算。
概念”Map(映射)”和”Reduce(归约)”,是它们的主要思想,都是从函数式编程语言里借来的,还有从矢量编程语言里借来的特性。
它极大地方便了编程人员在不会分布式并行编程的情况下,将自己的程序运行在分布式系统上。
当前的软件实现是指定一个Map(映射)函数,用来把一组键值对映射成一组新的键值对,指定并发的Reduce(归约)函数,用来保证所有映射的键值对中的每一个共享相同的键组。
关注博主不迷路,获取更多干货资源
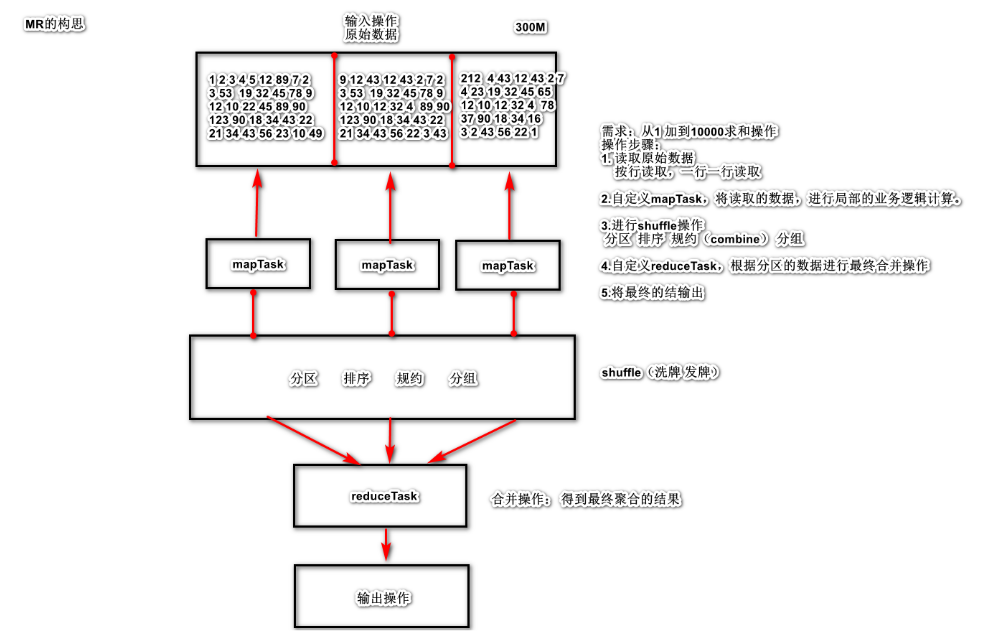
1 MapReduce基本概念
分布式计算框架,是hadoop的一部分。分而治之 ,比如人口普查
1.1 名词解释 1.1.1 Map
Map负责“分” ,即把复杂的任务分解为若干个“简单的任务”来并行处理。可以进行拆分的前提是这些小任务可以并行计算,彼此间几乎没有依赖关系。
这个具有强依赖关系,就不行
- 第一个人拿走:前300个同学的成绩 进行求平均分 ,等到平均分(70+80 +90 ...+92 .5)/300 = 80.5-2000 个同学成绩,等到(70+85 +90 ...+95 )/1701= 69-5000 个同学成绩,等到(73+81 +94 ...+92 )/3000= 74.5+69 +74 .5)/3 是真正的平均值吗 ? 肯定不是...
1.1.1 Reduce
Reduce负责“合” ,即对map阶段的结果进行全局汇总。
1.2 设计构思 1.2.1 如何对付大数据处理
对相互间不具有计算依赖关系的大数据,实现并行最自然的办法就是采取分而治之的策略。并行计算的第一个重要问题是如何划分计算任务或者计算数据以便对划分的子任务或数据块同时进行计算。不可分拆的计算任务或相互间有依赖关系的数据无法进行并行计算!
1.2.2 构建抽象模型
MapReduce借鉴了函数式语言中的思想,用Map和Reduce两个函数提供了高层的并行编程抽象模型。
Map: 对一组数据元素进行某种重复式的处理;
Reduce: 对Map的中间结果进行某种进一步的结果整理。
MapReduce中定义了如下的Map和Reduce两个抽象的编程接口,由用户去编程实现:
map: (k1; v1) → [(k2; v2)]
reduce: (k2; [v2]) → [(k3; v3)]
Map和Reduce为程序员提供了一个清晰的操作接口抽象描述。通过以上两个编程接口,大家可以看出MapReduce处理的数据类型是<key,value>键值对。
1.2.3 统一构架,隐藏系统层细节
如何提供统一的计算框架,如果没有统一封装底层细节,那么程序员则需要考虑诸如数据存储、划分、分发、结果收集、错误恢复等诸多细节;为此,MapReduce设计并提供了统一的计算框架,为程序员隐藏了绝大多数系统层面的处理细节。
MapReduce最大的亮点在于通过抽象模型和计算框架把需要做什么(what need to do)与具体怎么做(how to do)分开了,为程序员提供一个抽象和高层的编程接口和框架。程序员仅需要关心其应用层的具体计算问题,仅需编写少量的处理应用本身计算问题的程序代码。如何具体完成这个并行计算任务所相关的诸多系统层细节被隐藏起来,交给计算框架去处理:从分布代码的执行,到大到数千小到单个节点集群的自动调度使用。
1.3 核心功能
将用户编写的业务逻辑代码和MapReduce本身自带的组件整合到一个完整的分布式计算程序。
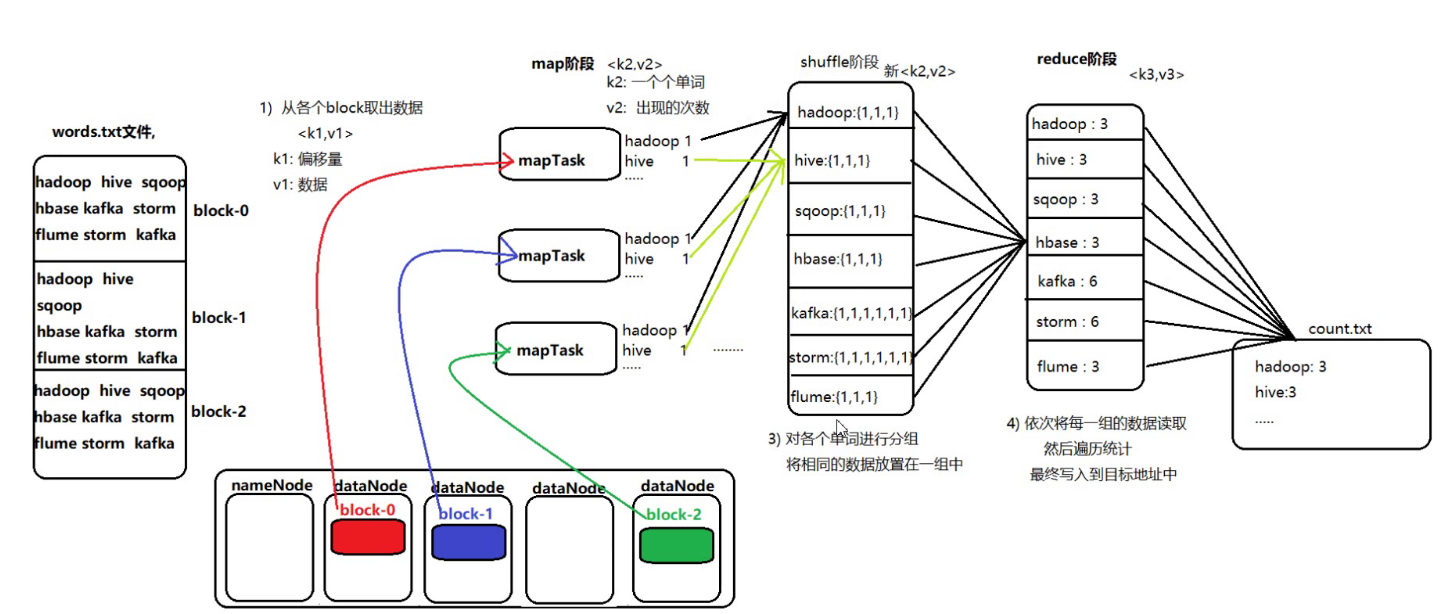
block 数据分块,是hdfs中的概念,物理上进行数据的分割,(默认128M)分成一个数据块,split是mapreduce中的一个逻辑的概念,mapTask处理数据的一个分片,具体怎么分片,是和 InputFormat。每个分片对应的是一个map任务。
2 MapReduce编程规范
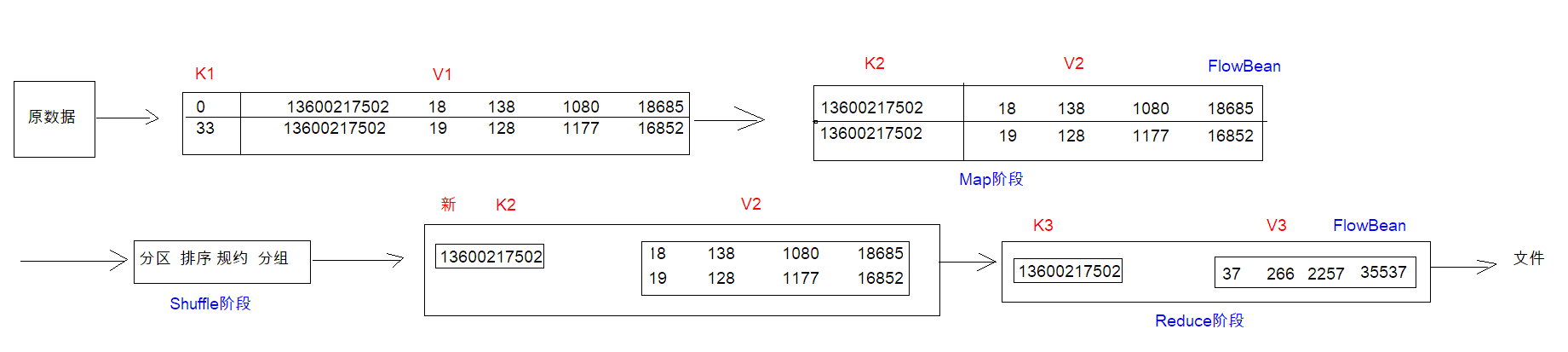
数据传输的过程中,都是以 key - value的键值对出现的。
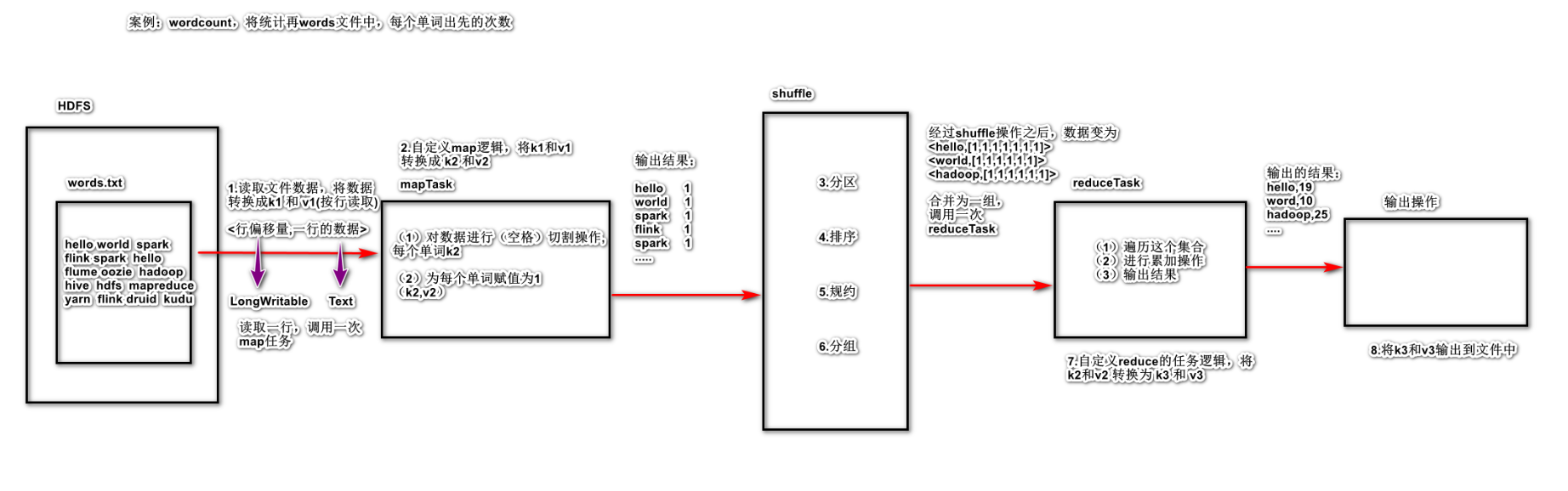
2.1 三个阶段 2.1.1 map阶段
读取数据,将数据转换成 k1 和 v1
自定义 map逻辑, 将 k1 和 v1 转换成 k2 和 v2
2.1.2 shuffle阶段
分区: 将相同的k2的数据发送给同一个reduce程序
排序:根据k2的数据,进行排序操作(按照字典顺序)
规约combine:是局部聚合,是MapReduce的优化步骤
分组:将相同的k2的值进行合并成为一个集合
2.1.3 reduce阶段
自定义 reduce 任务的逻辑,将 shuffle 的 k2 和v2 进行转换操作得到 k3 和 v3
输出操作:将k3 和v3 输出到指定的文件目录
2.2 编程步骤
用户编写的程序分成三个部分:Mapper,Reducer,Driver(提交运行mr程序的客户端)
2.2.1 Mapper (1)自定义类继承Mapper类
2.2.2 Reducer (1)自定义类继承Reducer类
2.2.3 Driver
整个程序需要一个Drvier来进行提交,提交的是一个描述了各种必要信息的job对象
(1)定义类,编写main方法
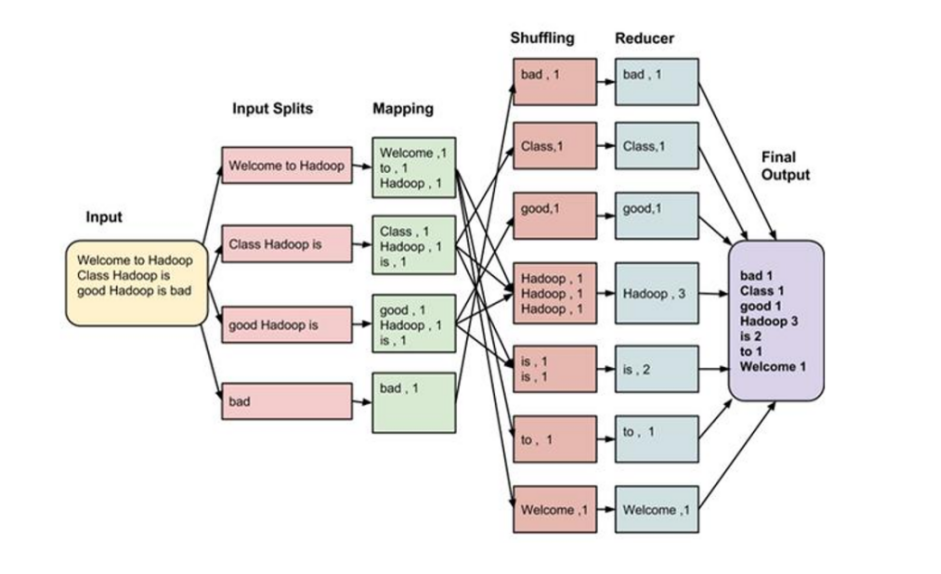
2.3 编程示例(单词统计) 2.3.1 实现思路
2.3.2 数据准备
1 创建新文件
cd /export/ server
2 向其中放入以下内容并保存
hello hello world world hadoop hadoop hello world hello flume hadoop hive hive kafka flume storm hive oozie
3 上传到 HDFS
hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /input/ wordcount/input/ wordcount
4 查看上传结果
2.3.3 代码实现
1.pom文件
点击查看pom
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns ="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd" > <parent > <artifactId > beijing45-parent</artifactId > <groupId > cn.itcast</groupId > <version > 1.0-SNAPSHOT</version > </parent > <modelVersion > 4.0.0</modelVersion > <artifactId > day09_mapreduce1</artifactId > <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.hadoop</groupId > <artifactId > hadoop-common</artifactId > <version > 2.7.5</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.hadoop</groupId > <artifactId > hadoop-client</artifactId > <version > 2.7.5</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.hadoop</groupId > <artifactId > hadoop-hdfs</artifactId > <version > 2.7.5</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.hadoop</groupId > <artifactId > hadoop-mapreduce-client-core</artifactId > <version > 2.7.6</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > junit</groupId > <artifactId > junit</artifactId > <version > 4.13</version > </dependency > </dependencies > <build > <plugins > <plugin > <groupId > org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId > <artifactId > maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId > <version > 3.0</version > <configuration > <source > 1.8</source > <target > 1.8</target > <encoding > UTF-8</encoding > </configuration > </plugin > <plugin > <groupId > org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId > <artifactId > maven-shade-plugin</artifactId > <version > 2.4.3</version > <executions > <execution > <phase > package</phase > <goals > <goal > shade</goal > </goals > <configuration > <minimizeJar > true</minimizeJar > </configuration > </execution > </executions > </plugin > </plugins > </build > </project >
2.WordCoutMapperTask.java
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 package cn.xiaoma.mapreduce;import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;import java.io.IOException;public class WordCoutMapperTask extends Mapper <LongWritable , Text ,Text , IntWritable > @Override protected void map (LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException "偏移量:" +key.get());if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(line)){" " );for (String word : words){new Text(word),new IntWritable(1 ));
3.WordCountReduceTask.java
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 package cn.xiaoma.mapreduce;import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;import java.io.IOException;public class WordCountReduceTask extends Reducer <Text , IntWritable ,Text , IntWritable > @Override protected void reduce (Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException int count = 0 ;for (IntWritable v2:values){new IntWritable(count));
4.WordCountMain.java
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 package cn.xiaoma.mapreduce;import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configured;import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.partition.HashPartitioner;import org.apache.hadoop.util.Tool;import org.apache.hadoop.util.ToolRunner;public class WordCountMain extends Configured implements Tool public static void main (String[] args) throws Exceptionnew Configuration();int code = ToolRunner.run(conf, new WordCountMain(), args);@Override public int run (String[] args) throws Exception super .getConf(), "wordcount" );new Path("F:\\Black_House_42\\Blk_BigData_42\\03_Hadoop\\day09_MapReduce\\资料\\wordcount\\input\\wordcount.txt" ));new Path("F:\\Black_House_42\\Blk_BigData_42\\03_Hadoop\\day09_MapReduce\\资料\\wordcount\\output\\wordcount.txt" ));boolean flag = job.waitForCompletion(true );return flag?0 :1 ;
3 MapReduce程序运行模式 3.1 本地运行模式
1 mapreduce程序是被提交给LocalJobRunner在本地以单进程的形式运行
3.2 集群运行模式
1 将mapreduce程序提交给yarn集群,分发到很多的节点上并发执行
集群运行程序
修改WordCountMain类中的下面两行代码如下图
TextInputFormat .InputPath(job ,new Path(args [0]) );TextOutputFormat .OutputPath(job ,new Path(args [1]) );
上面pom插件将这个jar包中所有依赖的第三方的 jar 包 导入到当前的jar包中,这个 jar 包就叫 肥包。
将这个 jar 包(不是带第三方依赖的小包)上传到 linux 中的任意目录(比如/root/)
在yarn集群中执行 mapreduce。
执行的脚本可以使用 hadoop jar (1.X) 也可以使用 yarn jar (2.x)运行。
当前wordcount的集群执行命令
1.0 -SNAPSHOT.jar cn.xiaoma.mapreduce.WordCountMain /input/ wordcount/wordcount.txt / output/wordcount/
start historyserver
4 MapReduce分区
分区: 将相同的 k2 的数据发送到同一个分区中
物以类聚,人与群分
在 MapReduce 中, 通过我们指定分区, 会将同一个分区的数据发送到同一个Reduce当中进行处理。例如: 为了数据的统计, 可以把一批类似的数据发送到同一个 Reduce 当中, 在同一个 Reduce 当中统计相同类型的数据, 就可以实现类似的数据分区和统计等
其实就是相同类型的数据, 有共性的数据, 送到一起去处理, 在Reduce过程中,可以根据实际需求(比如按某个维度进行归档,类似于数据库的分组),把Map完的数据Reduce到不同的文件中。分区的设置需要与ReduceTaskNum配合使用。比如想要得到5个分区的数据结果。那么就得设置5个ReduceTask。
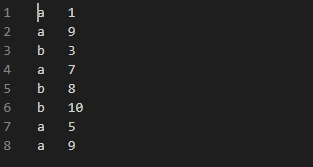
4.1 案例 4.1.1 分析 需求:将文本文件中的彩票数据进行分区,小于等于15的分到一个区里, 大于15的分到另外一个区里,并最终将数据保存到两个文件中。
思路:怎么进行数据的分区?
mapreduce 默认分区的方式是 hashPartiton
(key.hashCode() & Integer .MAX_VALUE) % numReduceTasks;
如何创建自定义分区
创建一个类,继承 Partitioner<K,V>
重写 getPartition 方法
自定义分区规则,小于等于1 5是个规则0,大于15是个规则1
在入口函数在中将分区规则设置到驱动类
4.1.2 实现
1.实现分区业务逻辑
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 package cn.xiaoma.partition;import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;public class MyPartition extends Partitioner <IntWritable , Text > @Override public int getPartition (IntWritable lotteryResult, Text text, int numPartitions) if (lotteryResult.get()<=15 ){return 0 ;else {return 1 ;
2.实现 map 业务逻辑
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 package cn.xiaoma.partition;import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;import java.io.IOException;public class LotteryMapperTask extends Mapper <LongWritable ,Text , IntWritable , Text > @Override protected void map (LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(line)){"\t" )[5 ];int code = Integer.parseInt(lotteryResult);new IntWritable(code),value);
3.实现 reduce 的业务逻辑
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 package cn.xiaoma.partition;import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;import java.io.IOException;public class LotteryReducerTask extends Reducer <IntWritable , Text ,Text , NullWritable > @Override protected void reduce (IntWritable key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException for (Text value:values){
4.实现LotteryMain的业务逻辑
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 package cn.xiaoma.partition;import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;public class LotteryMain public static void main (String[] args) throws Exceptionnew Configuration();"Lottery ticket MR" );new Path(args[0 ]));new Path(args[1 ]));2 );boolean flag = job.waitForCompletion(true );int i = flag ? 0 : 1 ;
5.数据准备
hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /input/partition put partition .txt /input/partition /partition .csv
6.执行 shell 脚本
yarn jar original-day09_mapreduce1-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar cn.xiaoma.partition.LotteryMain /input/partition/partition.csv /output/partition
5 MapReduce排序和序列化 5.1 概述 序列化(Serialization)是指把结构化对象转化为字节流。
反序列化(Deserialization)是序列化的逆过程。把字节流转为结构化对象。
Java的序列化(Serializable)是一个重量级序列化框架,一个对象被序列化后,会附带很多额外的信息(各种校验信息,header,继承体系…),不便于在网络中高效传输;所以,hadoop自己开发了一套序列化机制(Writable),精简,高效。不用像java对象类一样传输多层的父子关系,需要哪个属性就传输哪个属性值,大大的减少网络传输的开销。
5.1 案例
这个就不在服务器跑了,跑的流程都一样,看下上面的案例就好,换下文件的路径,yarn jar 跑一下就好了
5.1.1 需求
将数据进行排列,第一列降序排列,如果相等的情况下,第二列进行升序排列,输出到文件
5.1.2 分析
实现SortPojo 类 思路:
实现自定义的bean来封装数据,并将bean作为map输出的key来传输
MR程序在处理数据的过程中会对数据排序(map输出的kv对传输到reduce之前,会排序),排序的依据是map输出的key。所以,我们如果要实现自己需要的排序规则,则可以考虑将排序因素放到key中,让key实现接口:WritableComparable,然后重写key的compareTo方法。
5.1.3 实现
1.SortPojo类
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 package cn.itcast.sort;import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;import java.io.DataInput;import java.io.DataOutput;import java.io.IOException;public class SortPojo implements WritableComparable <SortPojo > private String first;private String second;public SortPojo () public String getFirst () return first;public void setFirst (String first) this .first = first;public String getSecond () return second;public void setSecond (String second) this .second = second;@Override public String toString () return first + "\t" +second;@Override public int compareTo (SortPojo o) int i = o.first.compareTo(this .first);if ( i == 0 ){int i1 = this .second.compareTo(o.second);return i1;return i;@Override public void write (DataOutput out) throws IOException @Override public void readFields (DataInput in) throws IOException this .first = in.readUTF();this .second = in.readUTF();
2.SortMapperTask 类的实现
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 package cn.itcast.sort;import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils ;import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable ;import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable ;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text ;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper ;import java.io.IOException ;class SortMapperTask extends Mapper<LongWritable , Text ,SortPojo , NullWritable> @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException , InterruptedException {String line = value.toString();if (StringUtils .isNotEmpty(line)){String [] sortPojoArr = line.split("\t" );SortPojo sortPojo = new SortPojo ();0 ]);1 ]);NullWritable .get());
3.SortReduceTask 的实现
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 package cn.itcast.sort;import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable ;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer ;import java.io.IOException ;class SortReduceTask extends Reducer<SortPojo , NullWritable ,SortPojo , NullWritable> @Override protected void reduce(SortPojo key, Iterable <NullWritable > values, Context context) throws IOException , InterruptedException {for (NullWritable n:values){
4.SortMain 类的实现
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 package cn.itcast.sort;class SortMain {[] args) throws Exception {new Configuration() ;Job .Instance(conf , "sort MR" ) ;InputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class ) ;TextInputFormat .InputPath(job ,new Path("F:\\Black_House_42\\Blk_BigData_42\\03_Hadoop\\day09_MapReduce\\资料\\排序\\input\\sort.txt" ) );MapperClass(SortMapperTask.class ) ;MapOutputKeyClass(SortPojo.class ) ;MapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class ) ;ReducerClass(SortReduceTask.class ) ;OutputKeyClass(SortPojo.class ) ;OutputValueClass(NullWritable.class ) ;OutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class ) ;TextOutputFormat .OutputPath(job ,new Path("F:\\Black_House_42\\Blk_BigData_42\\03_Hadoop\\day09_MapReduce\\资料\\排序\\output" ) );ForCompletion(true ) ;System .0 :1 );
6 MapReduce的combine规约 6.1 概念
每一个 map 都可能会产生大量的本地输出,Combiner 的作用就是对 map 端的输出先做一次合并,以减少在 map 和 reduce 节点之间的数据传输量,以提高网络IO 性能,是 MapReduce 的一种优化手段之一
combiner 是 MR 程序中 Mapper 和 Reducer 之外的一种组件
combiner 组件的父类就是 Reducer
combiner 和 reducer 的区别在于运行的位置
combiner 的意义就是对每一个 maptask 的输出进行局部汇总,以减小网络传输量
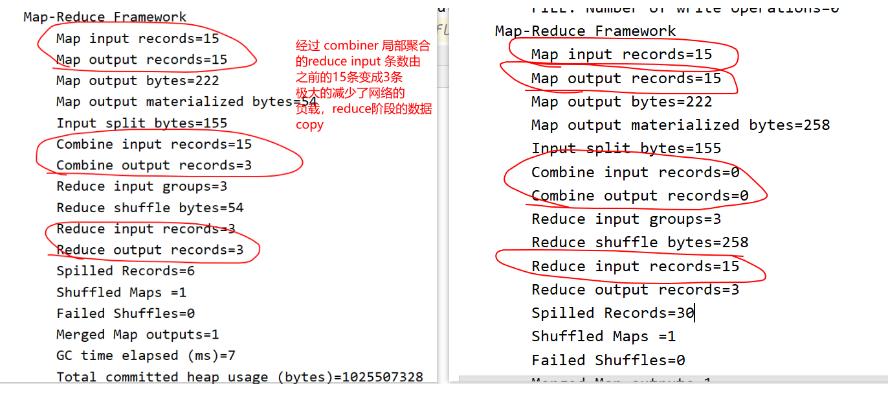
combine规约和reduce的逻辑是相似的,combine是一个本地局部(所有的所在节点)的汇总,以减小网络传输量;reduce是一个全局的汇总操作。
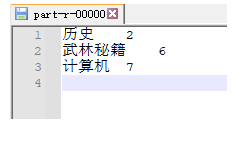
6.2 案例 6.2.1 需求 有三个书架 ,每个书架上都有5本书, 要求 统计出 每种分类的下有几本书?? 计算机 武林秘籍 历史
1号书架 2号书架 3号书架<<java入门宝典> > <<Python入门宝典> > <<spark入门宝典> ><<UI入门宝典> > <<乾坤大挪移> > <<hive入门宝典> > <<天龙八部> > <<凌波微步> > <<葵花点穴手> ><<史记> > <<PHP入门宝典> > <<铁砂掌> ><<葵花宝典> > <<hadoop入门宝典> > <<论清王朝的腐败> >
输入
<<java入门宝典> ><<Python入门宝典> ><<spark入门宝典> ><<UI入门宝典> ><<乾坤大挪移> ><<hive入门宝典> ><<天龙八部> ><<凌波微步> ><<葵花点穴手> ><<史记> ><<PHP入门宝典> ><<铁砂掌> ><<葵花宝典> ><<hadoop入门宝典> ><<论清王朝的腐败> >
6.2.2 分析
思路:
首先要创建 mapTask reduceTask
重写Reducer提供的reduce方法,实现局部聚合逻辑
在MR的驱动中,main函数中将 combine 的类添加进去。
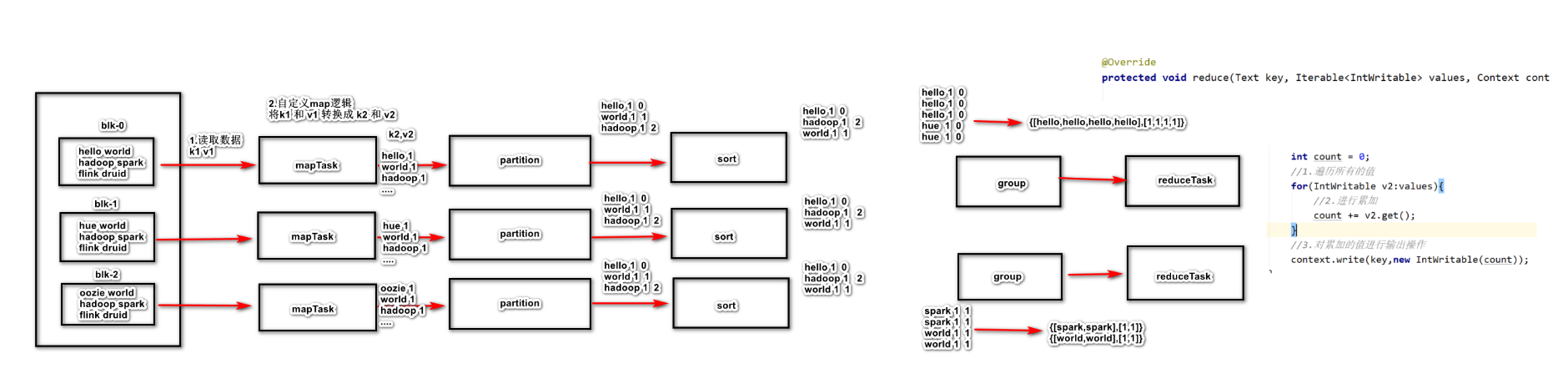
int count = 0 ;for (IntWritable value:values){count += value.get();write (key,new IntWritable(count ));
使用combiner 和不适用 combiner 的reduce端的数据 input 的区别,使用combiner 明显比不使用 combiner的读取数量要小。
6.2.3 实现
1.CombinerMapperTask
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 package cn.xiaoma.combine;import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;import java.io.IOException;public class CombinerMapperTask extends Mapper <LongWritable , Text , Text /*分类名称*/, IntWritable > @Override protected void map (LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(bookName)) {if (bookName.contains("入门" )) {new Text("计算机" ), new IntWritable(1 ));else if (bookName.contains("史记" ) || bookName.contains("论清王朝的腐败" )) {new Text("历史" ), new IntWritable(1 ));else {new Text("武林秘籍" ), new IntWritable(1 ));
2.CombinerReducerTask 实现
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 package cn.xiaoma.combine;import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;import java.io.IOException;public class CombinerReducerTask extends Reducer <Text , IntWritable , Text ,IntWritable > @Override protected void reduce (Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException int count = 0 ;for (IntWritable value:values){new IntWritable(count));
3.CombinerTask 的实现
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 package cn.xiaoma.combine;import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;import java.io.IOException;public class CombinerTask extends Reducer <Text , IntWritable ,Text ,IntWritable > @Override protected void reduce (Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException int count = 0 ;for (IntWritable value:values){new IntWritable(count));
4.CombinerJobMain 实现
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 package cn.xiaoma.combine;import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;public class CombinerJobMain public static void main (String[] args) throws Exceptionnew Configuration(), "combinerJobMR" );new Path("F:\\Black_House_42\\Blk_BigData_42\\03_Hadoop\\day10_MapReduce\\资料\\combinner\\input\\combiner.txt" ));new Path("F:\\Black_House_42\\Blk_BigData_42\\03_Hadoop\\day10_MapReduce\\资料\\combinner\\output" ));boolean flag = job.waitForCompletion(true );0 :1 );
6.2.4 运行结果
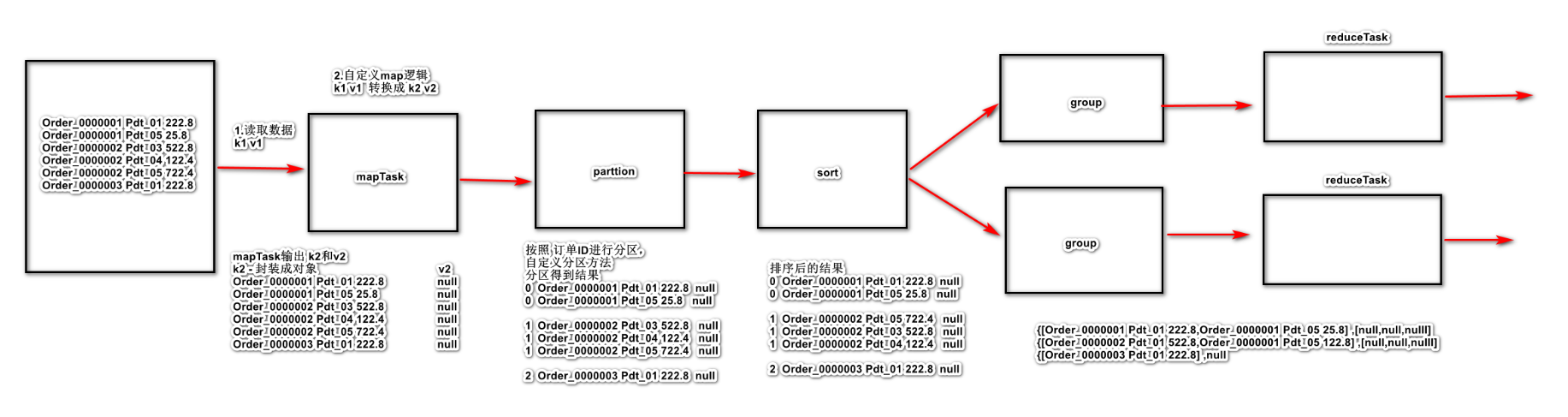
7 MapReduce的分组
分区和分组的区别
分区:将相同的 k2的数据,发送给同一个 reducer 中,这个操作是在 map端执行
分组:将相同的 k2的值进行合并形成一个集合操作,在 reduce 中对同一个分区下的数据进行分组操作。
7.1 需求 有如下订单数据,现在需要求出每一个订单中成交金额最大的一笔交易,将结果集存储到2个文件
订单id
商品id
成交金额
Order_0000001
Pdt_01
222.8
Order_0000001
Pdt_05
25.8
Order_0000002
Pdt_03
522.8
Order_0000002
Pdt_04
122.4
Order_0000002
Pdt_05
722.4
Order_0000003
Pdt_01
222.8
现在需要求出每一个订单中成交金额最大的一笔交易,将结果集存储到2个文件
7.2 分析 思路
如果使用 SQL 怎么写?
使用mapreduce 怎么来实现呢?
7.3 实现
1.OrderBean 实现
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 package cn.xiaoma.group;import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;import java.io.DataInput;import java.io.DataOutput;import java.io.IOException;public class OrderBean implements WritableComparable <OrderBean > private String orderid;private String pid;private Double price;public OrderBean () public String getOrderid () return orderid;public void setOrderid (String orderid) this .orderid = orderid;public String getPid () return pid;public void setPid (String pid) this .pid = pid;public Double getPrice () return price;public void setPrice (Double price) this .price = price;@Override public String toString () return orderid + "\t" + pid + "\t" + price;@Override public int compareTo (OrderBean o) int i = o.orderid.compareTo(this .orderid);if ( i == 0 ){int i1 = o.price.compareTo(this .price);return i1;return i;@Override public void write (DataOutput out) throws IOException @Override public void readFields (DataInput in) throws IOException this .orderid = in.readUTF();this .pid = in.readUTF();this .price=in.readDouble();
2.GroupMapperTask
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 package cn.xiaoma.group;import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;import java.io.IOException;public class GroupMapperTask extends Mapper <LongWritable , Text ,OrderBean , NullWritable > @Override protected void map (LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(line)){"\t" );new OrderBean();0 ]);1 ]);2 ]));
3.MyPartition
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 package cn.xiaoma.group;import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;public class MyPartition extends Partitioner <OrderBean , NullWritable > @Override public int getPartition (OrderBean orderBean, NullWritable nullWritable, int numPartitions) return (orderid.hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numPartitions;
4.MyGroup 分组实现
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 package cn.xiaoma.group;import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator;public class MyGroup extends WritableComparator public MyGroup () super (OrderBean.class,true );@Override public int compare (WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) return a1.getOrderid().compareTo(b1.getOrderid());
5.GroupReduceTask
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 package cn.xiaoma.group;import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;import java.io.IOException;public class GroupReduceTask extends Reducer <OrderBean , NullWritable , OrderBean , NullWritable > @Override protected void reduce (OrderBean key, Iterable<NullWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException int length = 1 ;for (NullWritable value : values) {if (length == 1 ) {break ;
6.GroupJobMain
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 package cn.xiaoma.group;import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;public class GroupJobMain public static void main (String[] args) throws Exceptionnew Configuration(), "GroupJobMR" );new Path(args[0 ]));new Path(args[1 ]));2 );boolean flag = job.waitForCompletion(true );0 :1 );
8 MapReduce的底层运行机制
mapTask的并行机制
mapTask在运行的时候,开启多个map由谁来决定?
默认情况:mapTask 的数量和读取 HDFS 中的数据块 block 的数量相等
block块:HDFS 中文件各个小数据块(默认 128m )(物理划分)
FileSplit: 在MapReduce 读取每一个块称为 fileSplit(文件切片)(逻辑划分)
block 的数量 和 文件分片的数量一样,大小也是一样。
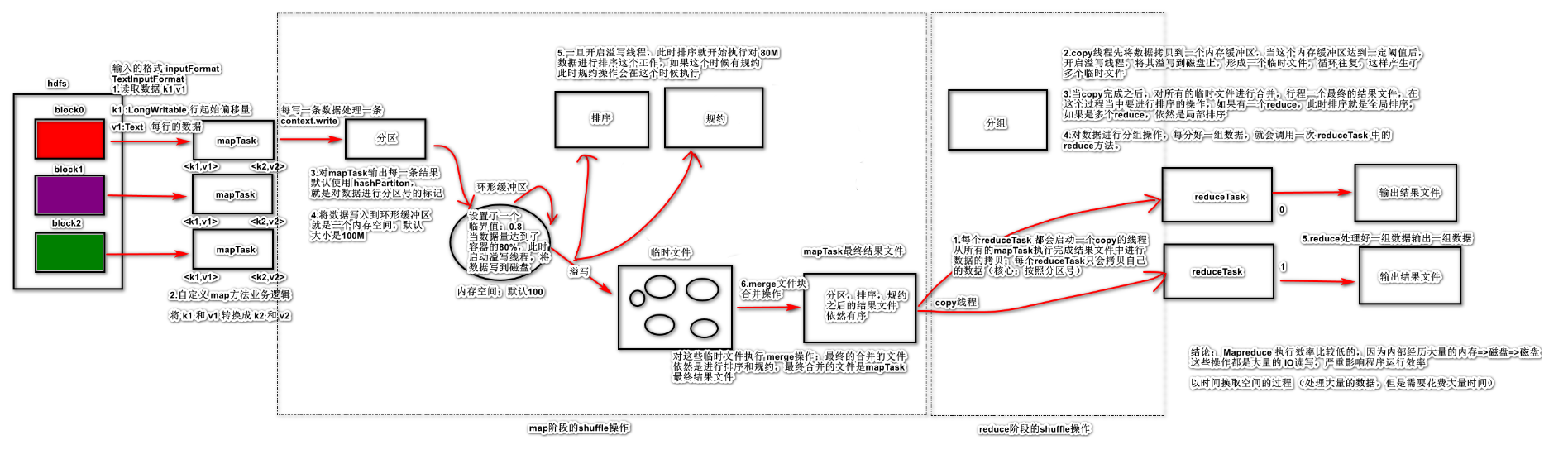
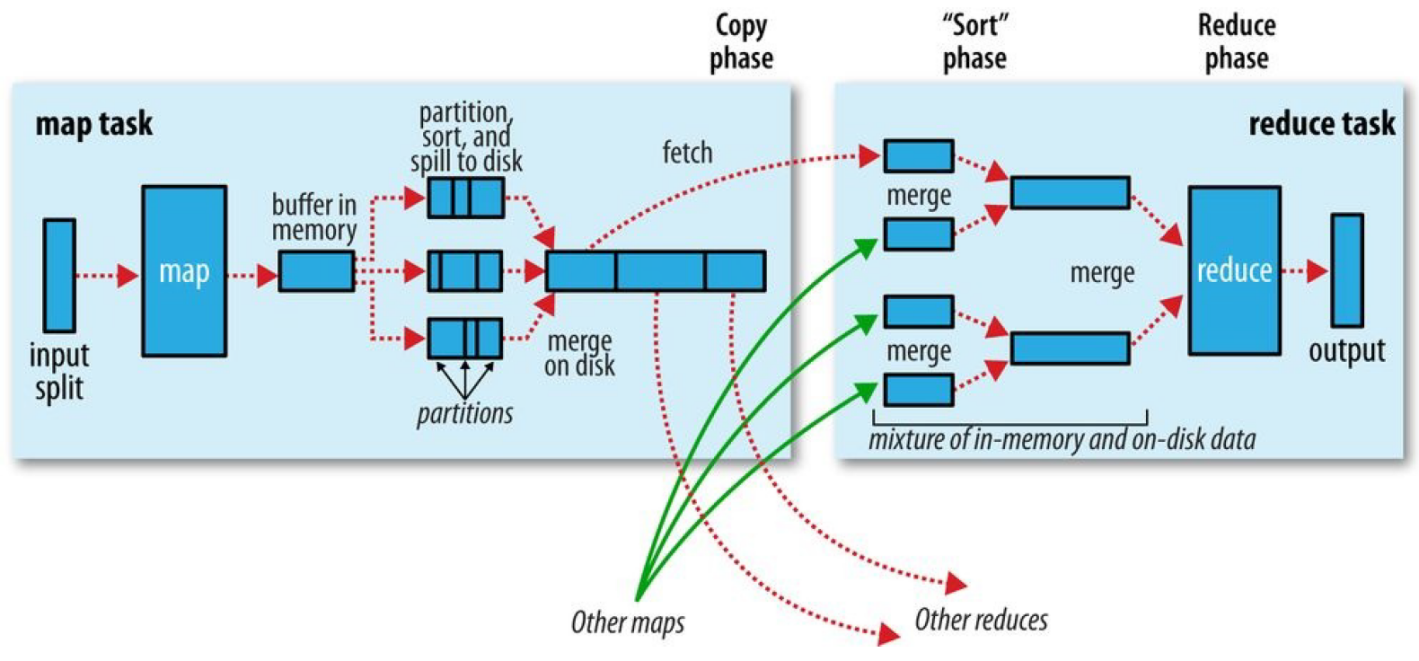
8.1 MapTask运行机制 简单概述:inputFile通过split被逻辑切分为多个split文件,通过Record按行读取内容给map(用户自己实现的)进行处理,数据被map处理结束之后交给OutputCollector收集器,对其结果key进行分区(默认使用hash分区),然后写入buffer,每个map task都有一个内存缓冲区,存储着map的输出结果,当缓冲区快满的时候需要将缓冲区的数据以一个临时文件的方式存放到磁盘,当整个map task结束后再对磁盘中这个map task产生的所有临时文件做合并,生成最终的正式输出文件,然后等待reduce task来拉数据。
8.1.1 详细步骤
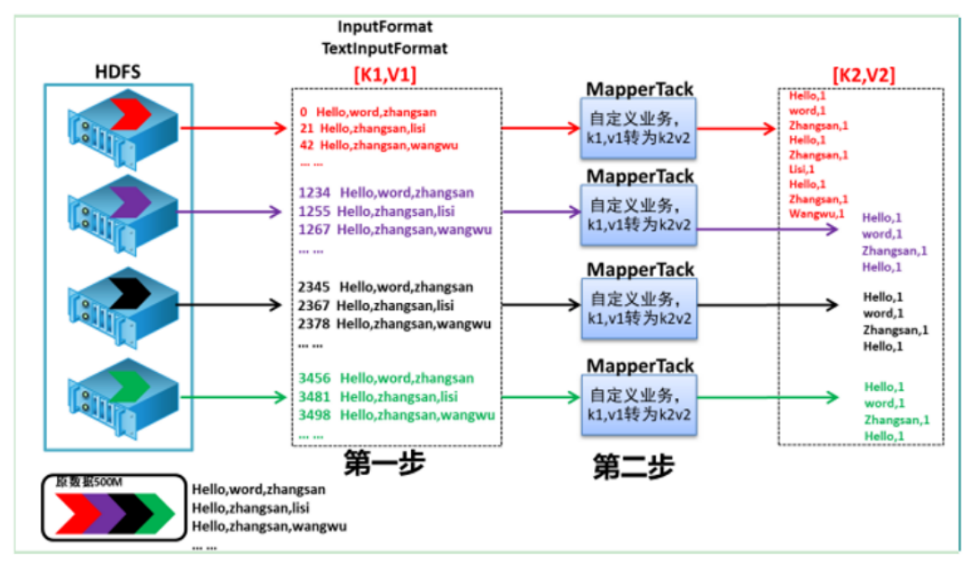
1 读取数据组件 InputFormat (默认 TextInputFormat) 会通过 getSplits 方法对输入目录中文件进行逻辑切片规划得到 block, 有多少个 block就对应启动多少个 MapTask.
2 将输入文件切分为 block 之后, 由 RecordReader 对象 (默认是LineRecordReader) 进行读取, 以 \n 作为分隔符, 读取一行数据, 返回 <key,value>. Key 表示每行首字符偏移值, Value 表示这一行文本内容
3 读取 block 返回 <key,value>, 进入用户自己继承的 Mapper 类中,执行用户重写的 map 函数, RecordReader 读取一行这里调用一次
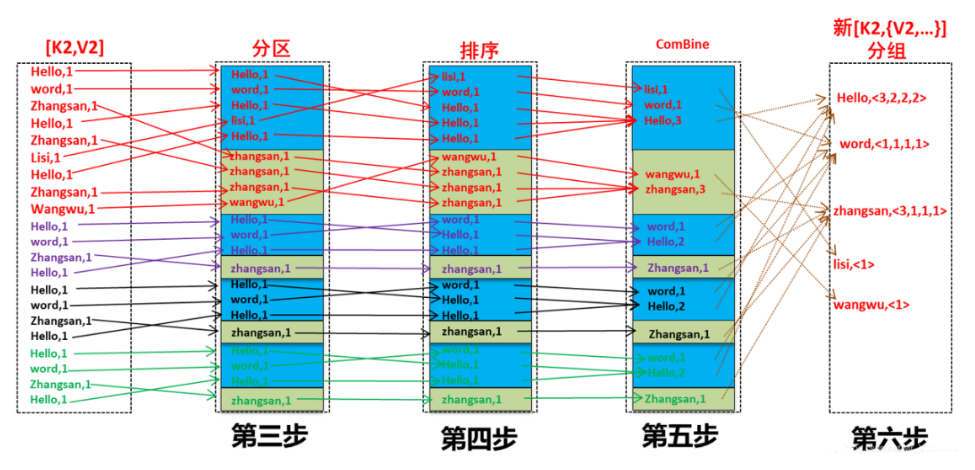
4 Mapper 逻辑结束之后, 将 Mapper 的每条结果通过 context.write 进行collect数据收集. 在 collect 中, 会先对其进行分区处理,默认使用 HashPartitioner
MapReduce 提供 Partitioner 接口, 它的作用就是根据 Key 或 Value 及 Reducer 的数量来决定当前的这对输出数据最终应该交由哪个 Reduce task 处理, 默认对 Key Hash 后再以 Reducer 数量取模. 默认的取模方式只是为了平均 Reducer 的处理能力, 如果用户自己对 Partitioner 有需求, 可以订制并设置到 Job 上
5 接下来, 会将数据写入内存, 内存中这片区域叫做环形缓冲区, 缓冲区的作用是批量收集 Mapper 结果, 减少磁盘 IO 的影响. 我们的 Key/Value 对以及 Partition 的结果都会被写入缓冲区. 当然, 写入之前,Key 与 Value 值都会被序列化成字节数组
环形缓冲区其实是一个数组, 数组中存放着 Key, Value 的序列化数据和 Key, Value 的元数据信息, 包括 Partition, Key 的起始位置, Value 的起始位置以及 Value 的长度. 环形结构是一个抽象概念
缓冲区是有大小限制, 默认是 100MB. 当 Mapper 的输出结果很多时, 就可能会撑爆内存, 所以需要在一定条件下将缓冲区中的数据临时写入磁盘, 然后重新利用这块缓冲区. 这个从内存往磁盘写数据的过程被称为 Spill, 中文可译为溢写. 这个溢写是由单独线程来完成, 不影响往缓冲区写 Mapper 结果的线程. 溢写线程启动时不应该阻止 Mapper 的结果输出, 所以整个缓冲区有个溢写的比例 spill.percent. 这个比例默认是 0.8, 也就是当缓冲区的数据已经达到阈值 buffer size * spill percent = 100MB * 0.8 = 80MB, 溢写线程启动, 锁定这 80MB 的内存, 执行溢写过程. Mapper 的输出结果还可以往剩下的 20MB 内存中写, 互不影响
6 当溢写线程启动后, 需要对这 80MB 空间内的 Key 做排序 (Sort). 排序是 MapReduce 模型默认的行为, 这里的排序也是对序列化的字节做的排序
如果 Job 设置过 Combiner, 那么现在就是使用 Combiner 的时候了. 将有相同 Key 的 Key/Value 对的 Value 加起来, 减少溢写到磁盘的数据量. Combiner 会优化 MapReduce 的中间结果, 所以它在整个模型中会多次使用
那哪些场景才能使用 Combiner 呢? 从这里分析, Combiner 的输出是 Reducer 的输入, Combiner 绝不能改变最终的计算结果. Combiner 只应该用于那种 Reduce 的输入 Key/Value 与输出 Key/Value 类型完全一致, 且不影响最终结果的场景. 比如累加, 最大值等. Combiner 的使用一定得慎重, 如果用好, 它对 Job 执行效率有帮助, 反之会影响 Reducer 的最终结果
7 合并溢写文件, 每次溢写会在磁盘上生成一个临时文件 (写之前判断是否有 Combiner), 如果 Mapper 的输出结果真的很大, 有多次这样的溢写发生, 磁盘上相应的就会有多个临时文件存在. 当整个数据处理结束之后开始对磁盘中的临时文件进行 Merge 合并, 因为最终的文件只有一个, 写入磁盘, 并且为这个文件提供了一个索引文件, 以记录每个reduce对应数据的偏移量
8.1.2 配置
配置
默认值
解释
mapreduce.task.io.sort.mb
100
设置环型缓冲区的内存值大小
mapreduce.map.sort.spill.percent
0.8
设置溢写的比例
mapreduce.cluster.local.dir
${hadoop.tmp.dir}/mapred/local
溢写数据目录
mapreduce.task.io.sort.factor
10
设置一次合并多少个溢写文件
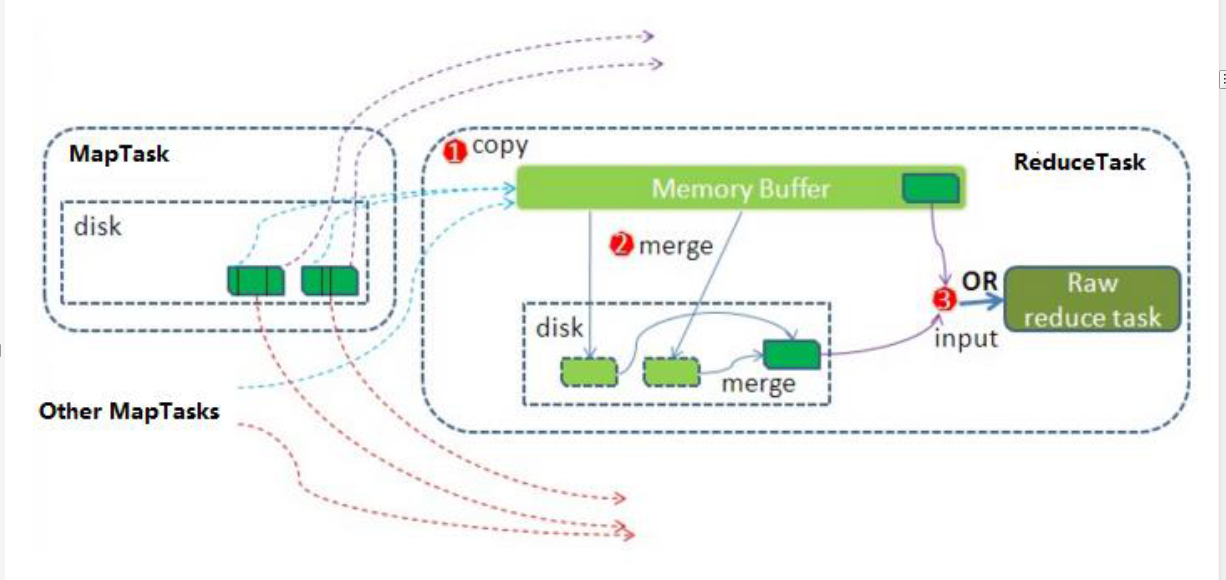
8.2 ReduceTask运行机制
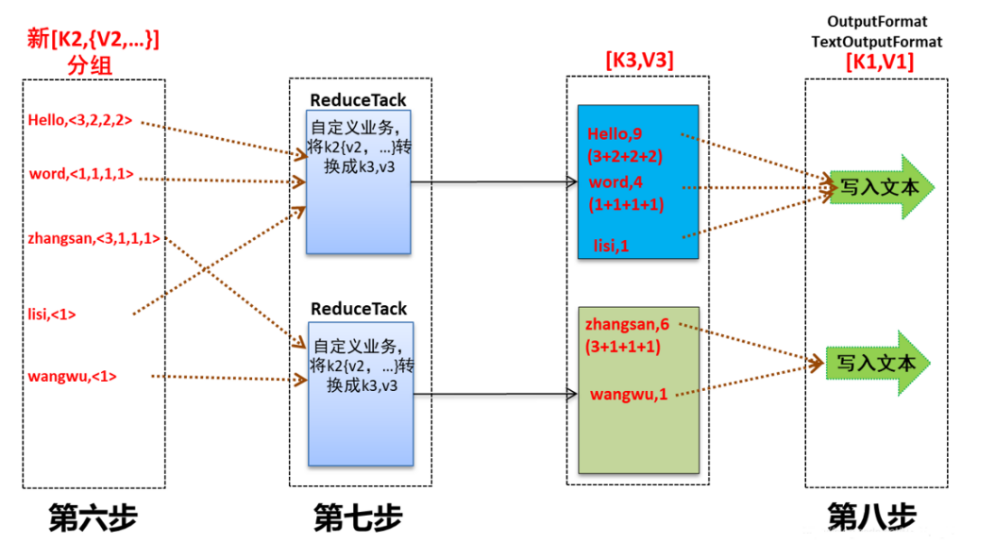
Reduce大致分为copy、sort、reduce三个阶段,重点在前两个阶段。copy阶段包含一个eventFetcher来获取已完成的map列表,由Fetcher线程去copy数据,在此过程中会启动两个merge线程,分别为inMemoryMerger和onDiskMerger,分别将内存中的数据merge到磁盘和将磁盘中的数据进行merge。待数据copy完成之后,copy阶段就完成了,开始进行sort阶段,sort阶段主要是执行finalMerge操作,纯粹的sort阶段,完成之后就是reduce阶段,调用用户定义的reduce函数进行处理。
详细步骤:
1 Copy阶段
简单地拉取数据。Reduce进程启动一些数据copy线程(Fetcher),通过HTTP方式请求maptask获取属于自己的文件。
2 Merge阶段
这里的merge如map端的merge动作,只是数组中存放的是不同map端copy来的数值。Copy过来的数据会先放入内存缓冲区中,这里的缓冲区大小要比map端的更为灵活。merge有三种形式:内存到内存;内存到磁盘;磁盘到磁盘。默认情况下第一种形式不启用。当内存中的数据量到达一定阈值,就启动内存到磁盘的merge。与map 端类似,这也是溢写的过程,这个过程中如果你设置有Combiner,也是会启用的,然后在磁盘中生成了众多的溢写文件。第二种merge方式一直在运行,直到没有map端的数据时才结束,然后启动第三种磁盘到磁盘的merge方式生成最终的文件。
3 合并排序
把分散的数据合并成一个大的数据后,还会再对合并后的数据排序。
4 对排序后的键值对调用reduce方法
键相等的键值对调用一次reduce方法,每次调用会产生零个或者多个键值对,最后把这些输出的键值对写入到HDFS文件中。
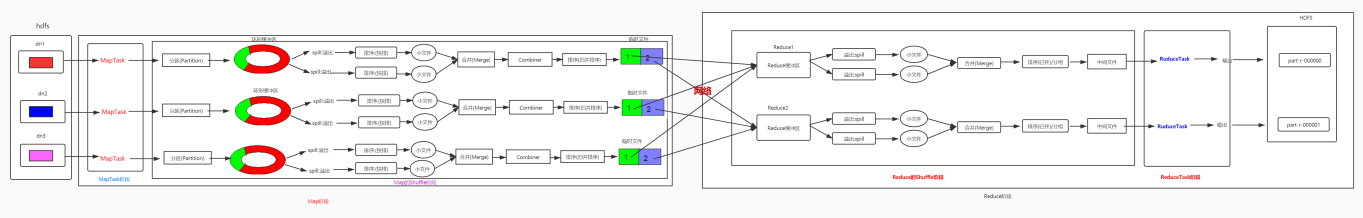
8.3 shuffle运行机制 map阶段处理的数据如何传递给reduce阶段,是MapReduce框架中最关键的一个流程,这个流程就叫shuffle。
shuffle是Mapreduce的核心,它分布在Mapreduce的map阶段和reduce阶段。一般把从Map产生输出开始到Reduce取得数据作为输入之前的过程称作shuffle。
1 Collect阶段
将MapTask的结果输出到默认大小为100M的环形缓冲区,保存的是key/value,Partition分区信息等。
2 Spill阶段
当内存中的数据量达到一定的阀值的时候,就会将数据写入本地磁盘,在将数据写入磁盘之前需要对数据进行一次排序的操作,如果配置了combiner,还会将有相同分区号和key的数据进行排序。
3 Merge阶段
把所有溢出的临时文件进行一次合并操作,以确保一个MapTask最终只产生一个中间数据文件。
4 Copy阶段
ReduceTask启动Fetcher线程到已经完成MapTask的节点上复制一份属于自己的数据,这些数据默认会保存在内存的缓冲区中,当内存的缓冲区达到一定的阀值的时候,就会将数据写到磁盘之上。
5 Merge阶段
在ReduceTask远程复制数据的同时,会在后台开启两个线程对内存到本地的数据文件进行合并操作。
6 Sort阶段
在对数据进行合并的同时,会进行排序操作,由于MapTask阶段已经对数据进行了局部的排序,ReduceTask只需保证Copy的数据的最终整体有效性即可。
Shuffle中的缓冲区大小会影响到mapreduce程序的执行效率,原则上说,缓冲区越大,磁盘io的次数越少,执行速度就越快
缓冲区的大小可以通过参数调整, 参数:mapreduce.task.io.sort.mb 默认100M
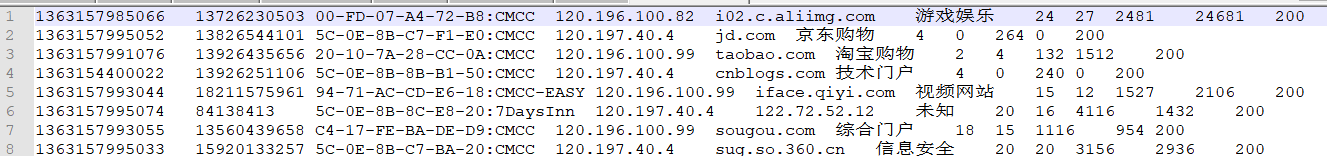
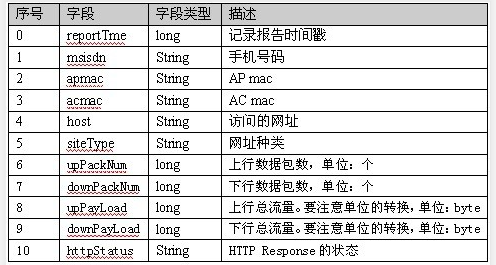
9 高阶案例 9.1 上网流量统计 数据格式如下:
9.1.1 统计求和 9.1.1.1 需求
统计上网流量中,每个手机号的上行流量、下行流量、上行总流量、下行总流量的和。
9.1.1.2 分析
9.1.1.3 实现
1.FlowBean
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 package cn.xiaoma.flow;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable;import java.io.DataInput;import java.io.DataOutput;import java.io.IOException;public class FlowBean implements Writable private Integer upFlow;private Integer downFlow;private Integer upCountFlow;private Integer downCountFlow;public FlowBean () public FlowBean (Integer upFlow, Integer downFlow, Integer upCountFlow, Integer downCountFlow) this .upFlow = upFlow;this .downFlow = downFlow;this .upCountFlow = upCountFlow;this .downCountFlow = downCountFlow;public Integer getUpFlow () return upFlow;public void setUpFlow (Integer upFlow) this .upFlow = upFlow;public Integer getDownFlow () return downFlow;public void setDownFlow (Integer downFlow) this .downFlow = downFlow;public Integer getUpCountFlow () return upCountFlow;public void setUpCountFlow (Integer upCountFlow) this .upCountFlow = upCountFlow;public Integer getDownCountFlow () return downCountFlow;public void setDownCountFlow (Integer downCountFlow) this .downCountFlow = downCountFlow;@Override public String toString () return upFlow +"\t" + downFlow+"\t" + upCountFlow+"\t" + downCountFlow;@Override public void write (DataOutput out) throws IOException @Override public void readFields (DataInput in) throws IOException this .upFlow = in.readInt();this .downFlow = in.readInt();this .upCountFlow = in.readInt();this .downCountFlow = in.readInt();
2.FlowMapperTask
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 package cn.xiaoma.flow;import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;import java.io.IOException;public class FlowMapperTask extends Mapper <LongWritable ,Text , Text /*手机号*/,FlowBean /*流量对象*/> @Override protected void map (LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(line)){"\t" );1 ];6 ];7 ];8 ];9 ];new FlowBean(new Text(iphone),flowBean);
3.FlowReduceTask
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 package cn.xiaoma.flow;import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;import java.io.IOException;public class FlowReduceTask extends Reducer <Text , FlowBean , Text , NullWritable > @Override protected void reduce (Text key, Iterable<FlowBean> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException 0 ;0 ;0 ;0 ;for (FlowBean value : values) {"\t" + upFlow + "\t" + downFlow + "\t" + upTotalFlow + "\t" + downTotalFlow;new Text(k3), NullWritable.get());
4.FlowJobMain
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 package cn.xiaoma.flow;import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;public class FlowJobMain public static void main (String[] args) throws Exceptionnew Configuration(), "FlowJobMR" );new Path(args[0 ]));new Path(args[1 ]));boolean flag = job.waitForCompletion(true );0 :1 );
9.1.2 上行流量倒序排序(递减排序) 9.1.2.1 需求
以需求一的输出数据作为排序的输入数据,自定义FlowBean,以FlowBean为map输出的key,以手机号作为Map输出的value,因为MapReduce程序会对Map阶段输出的key进行排序
1.定义FlowBean实现WritableComparable实现比较排序
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 public class FlowBean implements WritableComparable <FlowBean > private Integer upFlow;private Integer downFlow;private Integer upCountFlow;private Integer downCountFlow;public FlowBean () public FlowBean (Integer upFlow, Integer downFlow, Integer upCountFlow, Integer downCountFlow) this .upFlow = upFlow;this .downFlow = downFlow;this .upCountFlow = upCountFlow;this .downCountFlow = downCountFlow;@Override public void write (DataOutput out) throws IOException @Override public void readFields (DataInput in) throws IOException public Integer getUpFlow () return upFlow;public void setUpFlow (Integer upFlow) this .upFlow = upFlow;public Integer getDownFlow () return downFlow;public void setDownFlow (Integer downFlow) this .downFlow = downFlow;public Integer getUpCountFlow () return upCountFlow;public void setUpCountFlow (Integer upCountFlow) this .upCountFlow = upCountFlow;public Integer getDownCountFlow () return downCountFlow;public void setDownCountFlow (Integer downCountFlow) this .downCountFlow = downCountFlow;@Override public String toString () return upFlow+"\t" +downFlow+"\t" +upCountFlow+"\t" +downCountFlow;@Override public int compareTo (FlowBean o) return this .upCountFlow > o.upCountFlow ?-1 :1 ;
2.定义FlowMapper
点击查看代码
public class FlowMapper extends Mapper <LongWritable ,Text ,FlowBean ,Text > new Text();new FlowBean();@Override protected void map (LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException "\t" );1 ]));2 ]));3 ]));4 ]));0 ]);
3.定义FlowReducer
点击查看代码
public class FlowReducer extends Reducer <FlowBean ,Text ,Text ,FlowBean > new FlowBean();@Override protected void reduce (FlowBean key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException
4.程序main函数入口
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public class FlowMain extends Configured implements Tool @Override public int run (String[] args) throws Exception super .getConf();"mapreduce.framework.name" ,"local" );new Path("file:///D:\\flowcount\\output" ));new Path("file:///D:\\output\\flowcount_sort" ));boolean b = job.waitForCompletion(true );return b?0 :1 ;public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception new Configuration();int run = ToolRunner.run(configuration, new FlowMain(), args);
9.2 社交粉丝数据分析 数据如下:
以下是qq的好友列表数据,冒号前是一个用户,冒号后是该用户的所有好友(数据中的好友关系是单向的)
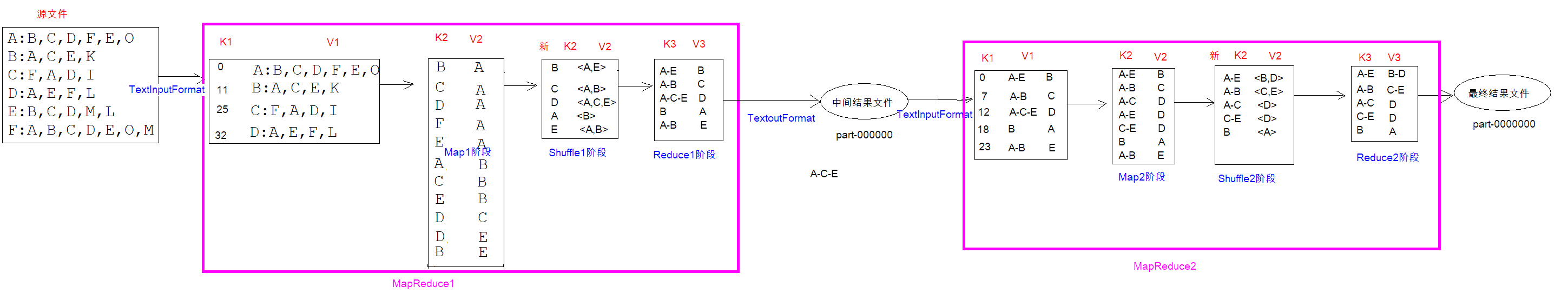
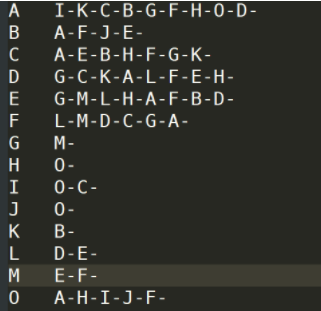
A : B , C , D , F , E , O B : A , C , E , K C : F , A , D , I D : A , E , F , L E : B , C , D , M , L F : A , B , C , D , E , O , M G : A , C , D , E , F H : A , C , D , E , O I : A , O J : B , O K : A , C , D L : D , E , F M : E , F , G O : A , H , I , J
9.2.1 需求
计算出来两两用户之间,有哪些共同好友?
9.2.2 分析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 # 案例数据A : B C D B : C D C : A B D D : A C # 某一个用户,在哪些好友列表中存在# 先mapper 任务< k1 , v1 > => < k2 , v2 > // k1 是偏移量, v1 是整个文本文件// 从左往右看, 是: B 出现在A 的好友列表, C 出现在A 的好友列表, D 出现在A 的好友列表< k2 , v2 > B A C A D A C B D B A C B C D C A D C D #reduce 任务// reduce 的任务就是对mapperde 结果进行归类统计B 出现在了A , C 的好友列表C 出现在了A , B , D 的好友列表D 出现在了A , B , C 的好友列表A 出现在了C , D 的好友列表B : { A , C } C : { A , B , D } D : { A , B , C } A : { C , D } # 写第二个MR #mapper 任务// A - B 的共同好友 c A - B 的共同好友 D A - C 的共同好友 B < k2 , V2 > A - B C A - B D A - C B A - C D A - D C B - C D B - D C C - D A #reduce 任务,先分组在聚合// 对mapper 的结果进行合并统计, 对相同的k2 进行value 的汇总A - B : { C , D } A - C : { B , D } A - D : { C } B - C : { D } B - D : { C } C - D : { A }
9.2.3 实现
1.Friend1MapperTask 实现
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 package cn.xiaoma.friend;import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;import java.io.IOException;public class Friend1MapperTask extends Mapper <LongWritable , Text ,Text ,Text > @Override protected void map (LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(line)){":" );1 ].split("," );for (String friend:friends){new Text(friend),new Text(splits[0 ]));
2.Friend1ReducerTask 实现
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 package cn.xiaoma.friend;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;import java.io.IOException;public class Friend1ReducerTask extends Reducer <Text ,Text ,Text ,Text > @Override protected void reduce (Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException "" ;for (Text friend:values){"-" ;new Text(v3));
3.Friend1JobMain
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 package cn.xiaoma.friend;import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;public class Friend1JobMain public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception new Configuration(), "Friend1JobMR" );new Path(args[0 ]));new Path(args[1 ]));boolean flag = job.waitForCompletion(true );0 :1 );
4.Friend2MapperTask
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 package cn.xiaoma.friend;import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;import java.io.IOException;import java.util.Arrays;public class Friend2MapperTask extends Mapper <LongWritable ,Text , Text ,Text > @Override protected void map (LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(line)){"\t" );1 ].split("-" );for (int i=0 ;i<friends.length-1 ;i++){for (int j=i+1 ;j<friends.length;j++){"-" + friends[j];new Text(k2),new Text(splits[0 ]));
5.Friend2ReducerTask
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 package cn.xiaoma.friend;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;import java.io.IOException;public class Friend2ReducerTask extends Reducer <Text ,Text ,Text ,Text > @Override protected void reduce (Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException "" ;for (Text value:values){"," ;new Text(v3));
6.Friend2JobMain 实现
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 package cn.xiaoma.friend;import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;public class Friend2JobMain public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception new Configuration(), "Friend2JobMR" );new Path(args[0 ]));new Path(args[1 ]));boolean flag = job.waitForCompletion(true );0 :1 );
总结: 第一个MR的文件的输出是第二个MR的输入,两个任务是串联的关系。
社交将某个人所有的好友列表显示出来
将最终两两之间的共同好友展示出来
9.3 倒序索引 9.3.1 倒排索引介绍
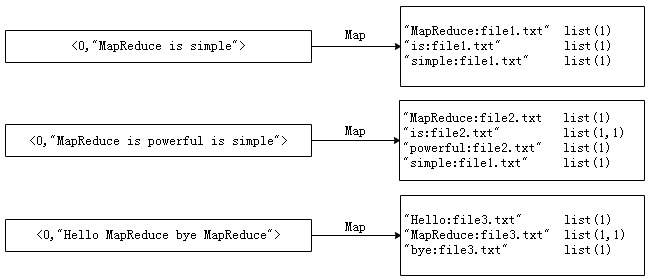
倒排索引 是文档检索系统中最常用的数据结构,被广泛应用于全文搜索引擎。倒排索引主要用来存储某个单词(或词组)在一组文档中的存储位置的映射,提供了可以根据内容来查找文档的方式,而不是根据文档来确定内容,因此称为倒排索引(Inverted Index)。带有倒排索引的文件我们称为倒排索引文件,简称倒排文件(Inverted File)。
通常情况下,倒排文件由一个单词(或词组)和相关联的文档列表组成,如图所示。
从图可以看出,建立倒排索引的目的是为了更加方便的搜索。例如,单词1出现在文档1、文档4、文档13等;单词2出现在文档2、文档6、文档10等;而单词3出现在文档3、文档7等。
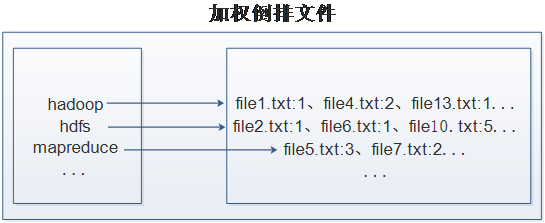
在实际应用中,还需要给每个文档添加一个权值,用来指出每个文档与搜索内容的相关度。最常用的是使用词频作为权重,即记录单词或词组在文档中出现的次数,用户在搜索相关文档时,就会把权重高的推荐给客户。下面以英文单词倒排索引为例,如图所示。
从图可以看出,加权倒排索引文件中,文件每一行内容对每一个单词进行了加权索引,统计出单词出现的文档和次数。例如索引文件中的第一行,表示“hadoop”这个单词在文本file1.txt中出现过1次,file4.txt中出现过2次,file13.txt中出现过1次。
9.3.2 案例需求及分析
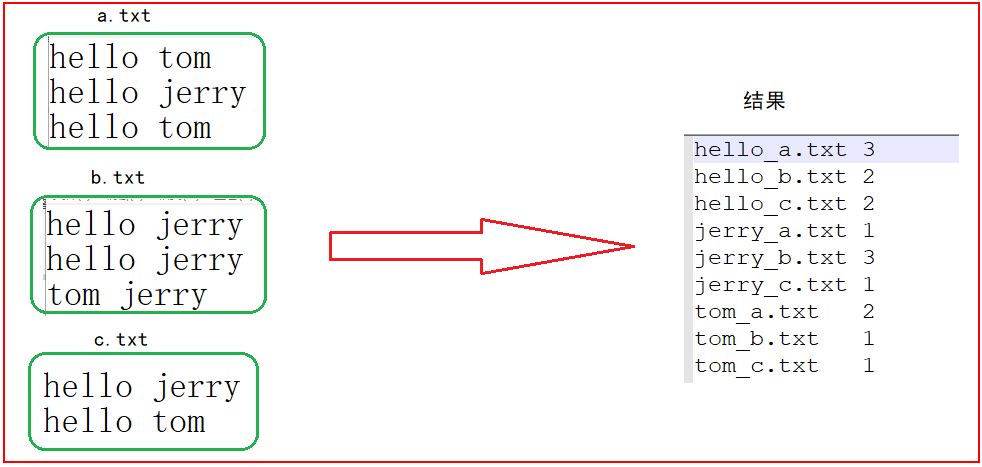
现假设有三个源文件a.txt、b.txt和c.txt,需要使用倒排索引的方式对这三个源文件内容实现倒排索引,并将最后的倒排索引文件输出,整个过程要求实现如下转换,如图所示。
接下来,我们就根据上面案例的需求结合倒排索引的实现,对该倒排索引案例的实现进行分析,具体如下。
首先使用默认的TextInputFormat类对每个输入文件进行处理,得到文本中每行的偏移量及其内容。Map过程首先分析输入的<key,value>键值对,经过处理可以得到倒排索引中需要的三个信息:单词、文档名称和词频,如图所示。
思路分析:
9.3.3 实现
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 public class IndexCreate extends Configured implements Tool public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception new Configuration(),new IndexCreate(),args);@Override public int run (String[] args) throws Exception super .getConf(), IndexCreate.class.getSimpleName());new Path("file:///F:\\传智播客大数据离线阶段课程资料\\倒排索引\\input" ));new Path("file:///F:\\传智播客大数据离线阶段课程资料\\5、大数据离线第五天\\倒排索引\\outindex" ));boolean bool = job.waitForCompletion(true );return bool?0 :1 ;public static class IndexCreateMapper extends Mapper <LongWritable ,Text ,Text ,IntWritable >new Text();new IntWritable(1 );@Override protected void map (LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException " " );for (String word : split) {"--" +name);public static class IndexCreateReducer extends Reducer <Text ,IntWritable ,Text ,IntWritable >new IntWritable();@Override protected void reduce (Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException int count = 0 ;for (IntWritable value : values) {
10 MapReduce并行读机制 10.1 MapTask并行读机制
MapTask的并行度指的是map阶段有多少个并行的task共同处理任务。map阶段的任务处理并行度,势必影响到整个job的处理速度。那么,MapTask并行实例是否越多越好呢?其并行度又是如何决定呢?
一个MapReducejob的map阶段并行度由客户端在提交job时决定,即客户端提交job之前会对待处理数据进行逻辑切片。切片完成会形成切片规划文件(job.split),每个逻辑切片最终对应启动一个maptask。
逻辑切片机制由FileInputFormat实现类的getSplits()方法完成。
FileInputFormat中默认的切片机制:
切片大小,默认等于block大小,即128M
block是HDFS上物理上存储的存储的数据,切片是对数据逻辑上的划分。
在FileInputFormat中,计算切片大小的逻辑:
Math.max (min Size, Math.min (max Size, block Size));
比如待处理数据有两个文件:
file1 .txt 320 Mfile2 .txt 10 M
经过FileInputFormat的切片机制运算后,形成的切片信息如下:
file1 .txt.split1 —0 M~128 Mfile1 .txt.split2 —128 M~256 Mfile1 .txt.split3 —256 M~320 Mfile2 .txt.split1 —0 M~10 M
FileInputFormat中切片的大小的由这几个值来运算决定:
在 FileInputFormat 中,计算切片大小的逻辑:
long splitSize = computeSplitSize(blockSize , minSize , maxSize )
切片主要由这几个值来运算决定:
blocksize:默认是 128 M,可通过 dfs.blocksize 修改1 ,可通过 mapreduce.input .fileinputformat .split .minsize 修改.input .fileinputformat .split .maxsize 修改
如果设置的最大值maxsize比blocksize值小,则按照maxSize切数据
如果设置的最小值minsize比blocksize值大,则按照minSize切数据
但是,不论怎么调参数,都不能让多个小文件“划入”一个 split
第一种情况(切片大小为256M):
FileInputFormat .InputPaths(job , new Path(input ) );MaxInputSplitSize(job ,1024* 1024* 500) ; FileInputFormat .MinInputSplitSize(job ,1024* 1024* 256) ;
第二种情况(切片大小为100M):
FileInputFormat .InputPaths(job , new Path(input ) );FileInputFormat .MaxInputSplitSize(job ,1024* 1024* 100) ; FileInputFormat .MinInputSplitSize(job ,1024* 1024* 80) ;
整个切片的核心过程在getSplit()方法中完成。
数据切片只是在逻辑上对输入数据进行分片,并不会再磁盘上将其切分成分片进行存储。InputSplit只记录了分片的元数据信息,比如起始位置、长度以及所在的节点列表等。
10.2 Reducetask并行度机制 reducetask并行度同样影响整个job的执行并发度和执行效率,与maptask的并发数由切片数决定不同,Reducetask数量的决定是可以直接手动设置:
如果数据分布不均匀,就有可能在reduce阶段产生数据倾斜。
注意: reducetask数量并不是任意设置,还要考虑业务逻辑需求,有些情况下,需要计算全局汇总结果,就只能有1个reducetask。
11 MapReduce性能优化策略
使用Hadoop进行大数据运算,当数据量极其大时,那么对MapReduce性能的调优重要性不言而喻,尤其是Shuffle过程中的参数配置对作业的总执行时间影响特别大。下面总结一些和MapReduce相关的性能调优方法,主要从五个方面考虑:数据输入、Map阶段、Reduce阶段、Shuffle阶段和其他调优属性。
11.1 数据输入
在执行MapReduce任务前,将小文件进行合并,大量的小文件会产生大量的map任务,增大map任务装载的次数,而任务的装载比较耗时,从而导致MapReduce运行速度较慢。因此我们采用CombineTextInputFormat来作为输入,解决输入端大量的小文件场景。
11.2 Map阶段
(1)减少溢写(spill)次数:通过调整io.sort.mb及sort.spill.percent参数值,增大触发spill的内存上限,减少spill次数,从而减少磁盘IO。
(2)减少合并(merge)次数:通过调整io.sort.factor参数,增大merge的文件数目,减少merge的次数,从而缩短mr处理时间。
(3)在map之后,不影响业务逻辑前提下,先进行combine处理,减少 I/O。
属性名称
类型
默认值
说明
mapreduce.task.io.sort.mb
int
100
配置排序map输出时使用的内存缓冲区的大小,默认100Mb,实际开发中可以设置大一些。
mapreduce.map.sort.spill.percent
float
0.80
map输出内存缓冲和用来开始磁盘溢出写过程的记录边界索引的阈值,即最大使用环形缓冲内存的阈值。一般默认是80%。也可以直接设置为100%
mapreduce.task.io.sort.factor
int
10
排序文件时,一次最多合并的流数,实际开发中可将这个值设置为100。
mapreduce.task.min.num.spills.for.combine
int
3
运行combiner时,所需的最少溢出文件数(如果已指定combiner)
11.3 Reduce阶段
(1)合理设置map和reduce数:两个都不能设置太少,也不能设置太多。太少,会导致task等待,延长处理时间;太多,会导致 map、reduce任务间竞争资源,造成处理超时等错误。
(2)设置map、reduce共存:调整slowstart.completedmaps参数,使map运行到一定程度后,reduce也开始运行,减少reduce的等待时间。
(3)规避使用reduce:因为reduce在用于连接数据集的时候将会产生大量的网络消耗。通过将MapReduce参数setNumReduceTasks设置为0来创建一个只有map的作业。
(4)合理设置reduce端的buffer:默认情况下,数据达到一个阈值的时候,buffer中的数据就会写入磁盘,然后reduce会从磁盘中获得所有的数据。也就是说,buffer和reduce是没有直接关联的,中间多一个写磁盘->读磁盘的过程,既然有这个弊端,那么就可以通过参数来配置,使得buffer中的一部分数据可以直接输送到reduce,从而减少IO开销。这样一来,设置buffer需要内存,读取数据需要内存,reduce计算也要内存,所以要根据作业的运行情况进行调整。
我们在上面提到的属性参数,都是位于mapred-default.xml文件中,这些属性参数的调优方式如表所示。
属性名称
类型
默认值
说明
mapreduce.job.reduce.slowstart.completedmaps
float
0.05
当map task在执行到5%,就开始为reduce申请资源。开始执行reduce操作,reduce可以开始拷贝map结果数据和做reduce shuffle操作。
mapred.job.reduce.input.buffer.percent
float
0.0
在reduce过程,内存中保存map输出的空间占整个堆空间的比例。如果reducer需要的内存较少,可以增加这个值来最小化访问磁盘的次数。
11.4 Shuffle阶段
Shuffle阶段的调优就是给Shuffle过程尽量多地提供内存空间,以防止出现内存溢出现象,可以由参数mapred.child.java.opts来设置,任务节点上的内存大小应尽量大。
我们在上面提到的属性参数,都是位于mapred-site.xml文件中,这些属性参数的调优方式如表所示。
属性名称
类型
默认值
说明
mapred.map.child.java.opts
-Xmx200m
当用户在不设置该值情况下,会以最大1G jvm heap size启动map task,有可能导致内存溢出,所以最简单的做法就是设大参数,一般设置为-Xmx1024m
mapred.reduce.child.java.opts
-Xmx200m
当用户在不设置该值情况下,会以最大1G jvm heap size启动Reduce task,也有可能导致内存溢出,所以最简单的做法就是设大参数,一般设置为-Xmx1024m
11.5 其他调优属性 除此之外,MapReduce还有一些基本的资源属性的配置,这些配置的相关参数都位于mapred-default.xml文件中,我们可以合理配置这些属性提高MapReduce性能,表4-4列举了部分调优属性。
属性名称
类型
默认值
说明
mapreduce.map.memory.mb
int
1024
一个Map Task可使用的资源上限。如果Map Task实际使用的资源量超过该值,则会被强制杀死。
mapreduce.reduce.memory.mb
int
1024
一个Reduce Task可使用的资源上限。如果Reduce Task实际使用的资源量超过该值,则会被强制杀死。
mapreduce.map.cpu.vcores
int
1
每个Map task可使用的最多cpu core数目
mapreduce.reduce.cpu.vcores
int
1
每个Reduce task可使用的最多cpu core数目
mapreduce.reduce.shuffle.parallelcopies
int
5
每个reduce去map中拿数据的并行数。
mapreduce.map.maxattempts
int
4
每个Map Task最大重试次数,一旦重试参数超过该值,则认为Map Task运行失败
mapreduce.reduce.maxattempts
int
4
每个Reduce Task最大重试次数,一旦重试参数超过该值,则认为Map Task运行失败
关注博主不迷路